Category:Conductivity & superconductivity: Difference between revisions
From ETHW
m (New page: IEEE GHN Category Category:Engineered materials & dielectrics) |
m (Text replace - "[[Category:Engineered_materials_&_dielectrics" to "[[Category:Materials") |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
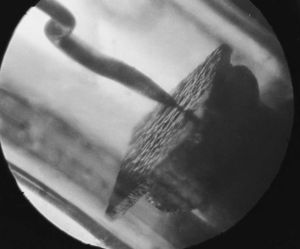
[[Image:Puntcontactdiode.jpg|thumb|right|Point-contact diode, inner structure. The rectangle is n-type semiconductor, and is about half a millimeter wide]] | |||
Topics related to electrical conductivity, including semiconductors, superconductors and current | |||
== Subcategories == | |||
*'''[[:Category:Semiconductor materials|Semiconductor materials]]''' - materials that have an intermediate electrical conductivity between a conductor and an insulator | |||
*'''[[:Category:Superconducting devices|Superconducting devices]]''' - devices that allow zero or almost zero electrical resistance, often operated at very low temperatures and with materials such as mercury | |||
*'''[[:Category:Superconducting integrated circuits|Superconducting integrated circuits]]''' - integrated circuits or ICs that have superconducting properties | |||
*'''[[:Category:Superconducting magnetic energy storage|Superconducting magnetic energy storage]]''' - or SMES, a system that stores energy in a magnetic field created by the flow of direct current through a superconducting coil cooled below its critical temperatures | |||
*'''[[:Category:Superconducting materials|Superconducting materials]]''' - materials, which, below a critical temperature, have zero or almost zero electrical resistance | |||
*'''[[:Category:Superconducting transition temperature|Superconducting transition temperature]]''' - the temperature at which a particular material becomes a superconductor with no electrical resistance | |||
*'''[[:Category:Wire|Wire]]''' - a single usually flexible strand of metal that transmits electricity and electromagnetic signals | |||
[[Category:Materials|{{PAGENAME}}]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:20, 25 July 2014
Topics related to electrical conductivity, including semiconductors, superconductors and current
Subcategories
- Semiconductor materials - materials that have an intermediate electrical conductivity between a conductor and an insulator
- Superconducting devices - devices that allow zero or almost zero electrical resistance, often operated at very low temperatures and with materials such as mercury
- Superconducting integrated circuits - integrated circuits or ICs that have superconducting properties
- Superconducting magnetic energy storage - or SMES, a system that stores energy in a magnetic field created by the flow of direct current through a superconducting coil cooled below its critical temperatures
- Superconducting materials - materials, which, below a critical temperature, have zero or almost zero electrical resistance
- Superconducting transition temperature - the temperature at which a particular material becomes a superconductor with no electrical resistance
- Wire - a single usually flexible strand of metal that transmits electricity and electromagnetic signals
Subcategories
This category has the following 7 subcategories, out of 7 total.
Pages in category "Conductivity & superconductivity"
The following 82 pages are in this category, out of 82 total.
A
G
H
K
M
S
- J. Robert Schrieffer
- Archives:A Review of UK Government Involvement in the Field of Semiconductor Technology Within the Research Establishments
- Archives:Diversity, Complementarity, and Cooperation Materials Innovation in the Semiconductor Industry
- Semiconductors
- Archives:From Germanium to Silicon, A History of Change in the Technology of the Semiconductors
- First-Hand:Serendipity and Superconducting Magnets
- Oral-History:Ralph M. Showers
- Oral-History:Arnold Silver
- Oral-History:George E. Smith
- Oral-History:Earl Steele
- Oral-History:Takuo Sugano
- IEEE Council on SuperConductivity History
- Superconductors
- Superinsulators