ARPANET: Difference between revisions
From ETHW
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''''This article is a stub. You can help the GHN by expanding it.''''' | <p>'''''This article is a stub. You can help the GHN by expanding it.''''' </p> | ||
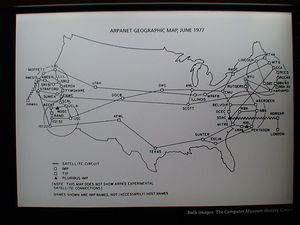
<p>[[Image:ARAPNET1977.jpg|thumb|left]]</p> | |||
[[Category:Computers_and_information_processing]] [[Category:Distributed_computing]] [[Category:Internet]] | <p>United States. In January 1969 ARPA awarded a contract to Bolt, [[Leo Beranek Oral History (1996)|Beranek]] and Newman (BBN) to design and construct a communications network. By the end of 1969, an experimental ARPANET was operational between four university nodes. The idea is based on Lawrence G. Roberts' 1966 publication, "Towards a Cooperative Network of Time-Shared Computers." </p> | ||
<p></p> | |||
<p>[[Category:Computers_and_information_processing]] [[Category:Distributed_computing]] [[Category:Internet]]</p> | |||
Revision as of 14:52, 14 July 2010
This article is a stub. You can help the GHN by expanding it.
United States. In January 1969 ARPA awarded a contract to Bolt, Beranek and Newman (BBN) to design and construct a communications network. By the end of 1969, an experimental ARPANET was operational between four university nodes. The idea is based on Lawrence G. Roberts' 1966 publication, "Towards a Cooperative Network of Time-Shared Computers."