William Emmet: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | == Biography == | ||
<p>[[Image:Emmet1.jpg|thumb|right]] </p> | |||
<p>[[Image:05-59 Rotary Converter.GIF|thumb|right|Rotary Converter]] </p> | |||
<p>Born: 10 July 1859<br>Died: 26 September 1941 </p> | |||
<p>William Le Roy Emmet was born in New Rochelle, New York, in 1859. He graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy in 1881 and served a tour on the ''U.S.S. Essex'' before leaving the Navy in 1883. </p> | |||
<p>His first experience in the field of electric power was gained with the United States Illuminating Company, which he left to join the [[Frank J. Sprague|Sprague]] Electric Railway and Motor Company in 1888. At Sprague, Emmet worked on the installation of electric street railway systems in several cities, including Cleveland, St. Louis, Wichita, and Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. Subsequently, he worked briefly for the [[George Westinghouse|Westinghouse]] Electric and Manufacturing Company and for the Buffalo Railway Company, before joining the Edison General Electric Company as district engineer in the Chicago district in 1891. When the [[General Electric (GE)|General Electric Company]] (GE) was formed through a merger of Edison General Electric and Thomson-Houston, Emmet became a GE employee and was assigned to the Lighting Department in Schenectady, New York, in 1894. </p> | |||
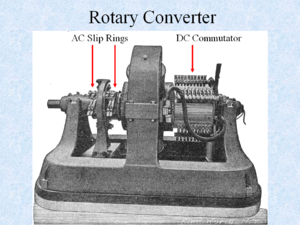
<p>Emmet made significant contributions to ac power systems including the design of large rotary converters which were used widely to convert transmitted ac power to direct current needed for the manufacture of aluminum, electric railways, and other applications. He was a leader in constructing the second largest power generating plant at Niagara Falls, New York, which used GE apparatus. </p> | |||
<p>His career was interrupted by the Spanish-American War when he served as a navigational officer on the collier ''Justin''. When he returned to GE, he was assigned to help develop the steam turbine which began to supplant reciprocating steam engines in the power generating field in the first decade of the twentieth century. Emmet directed the construction and installation of a 5,000 kW turboalternator at the Fisk Street power plant of the Chicago Edison Company in 1903. </p> | |||
<p>Emmet became a leading advocate of the electric propulsion of ships and his efforts led to a GE contract to equip the Navy collier Jupiter with turboelectric drive. The Jupiter proved quite successful during World War I and later was converted into an aircraft carrier and renamed the Langley. In 1915, GE received a contract to install the Emmet propulsion system on a new battleship, the ''New Mexico'', known initially as the California. First tested in sea trials in 1918, the ship's propulsion system, could deliver up to 32,000 hp and achieve a speed of 21 kn. Subsequently, GE installed an even more powerful drive system in high-speed battle cruisers known as the ''Saratoga'' and the ''Lexington''. These ships, later converted to aircraft carriers, were designed with 180,000 hp turboalternator propulsion and a speed of 35 kn. During World War I, Emmet served as a member of the Naval Consulting Board formed to provide expert advice on military innovations. </p> | |||
<p>Toward the end of his career, Emmet devoted a great deal of time and energy to the development and promotion of mercury vapor turbine, "as a more efficient power generation system than steam turbines." A few mercury turbines were installed as a result of his efforts but the difficulties and risks in using the new technology led to termination of the development after his retirement. </p> | |||
<p>He received the prestigious [[IEEE Edison Medal|Edison Medal of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers]] in 1919 'For inventions and developments of electrical apparatus and primo movers.' He received the Elliott Cresson Medal of the Franklin Institute in 1920 and also was elected to the National Academy Sciences. </p> | |||
<p>Emmet published ''The Autobiography of an Engineer ''in 1931. The book provided a personal account of his career of almost half a century devoted to electrical power engineering. In the preface, Emmet characterized engineering as a "thrilling profession to those who are suited to it, full of dangers, hopes, worries, and gratifications." Later in the book, he attributed much of his success to "a definiteness of purpose backed by a dogged perseverance." He added that "the important part of engineering is the detail and the good engineers are those who keep their eye close to it." He mentioned that he had always had a keen interest in other areas than engineering including literature, history, science, philosophy, music, and art in various forms." Emmet never married. He died on 26 September 1941 at age 82. </p> | |||
== Additional Information and Professional Honors == | |||
(A'93, M'94, member for life) | |||
'''Honorary Member 1933''' | |||
'''Edison Medalist 1919''' | |||
Emmet | AT THE time William LeRoy Emmet began his career in the electrical industry some 50 years ago, he was noted for his desire to explore new fields of engineering, rather than to work in those in which considerable development work had been done. This characteristic has continued throughout his life. Doctor Emmet was born in Pelham, N . Y., July 10, 1859. In 1881 he graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy, remaining in the Navy for 2 years thereafter. In 1887 he joined the Sprague Electric Company, then engaged in the historic electric railway developments at Richmond. Va., and at other cities. After short periods with the Westinghouse Electric and Manufacturing Company and the Buffalo (N.Y.) Railway Company he went to Chicago as district engineer for the newly formed Edison General Electric Company. In 1892 he was transferred to the New York office of the company, which later became the General Electric Company. In 1900 Doctor Emmet started his work on the Curtis steam turbine, and he continued its development until recent years, when his attention turned to the mercury vapor power process in which activity he has again been singularly successful. He is now a consulting engineer of the General Electric Company. Doctor Emmet was elected an Honorary Member of the Institute May 22, 1933, and in 1919 received the Edison Medal. Other medals have been awarded him. He has served the Institute on several of its committees, and was vice-president 1900-02. He is also a past vice-president of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. | ||
== Further Reading == | |||
[[Archives:Papers of W.L.R. Emmet|Papers of W.L.R. Emmet]] - records and correspondence, 1893 - 1941 | |||
"W. L. Emmet, 82, Engineer, Is Dead," ''New York Times'', Sep. 27, 1941. | <p>"W. L. Emmet, 82, Engineer, Is Dead," ''New York Times'', Sep. 27, 1941. </p> | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:People and organizations|Emmet]] [[Category:Power, energy & industry application|Emmet]] [[Category:Power engineering|Emmet]] [[Category:Electrification|Emmet]] [[Category:Power electronics|Emmet]] [[Category:Converters|Emmet]] [[Category:Power generation|Emmet]] [[Category:Hydroelectric power generation|Emmet]] [[Category:News|Emmet]] | ||
Revision as of 19:09, 4 April 2013
Biography
Born: 10 July 1859
Died: 26 September 1941
William Le Roy Emmet was born in New Rochelle, New York, in 1859. He graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy in 1881 and served a tour on the U.S.S. Essex before leaving the Navy in 1883.
His first experience in the field of electric power was gained with the United States Illuminating Company, which he left to join the Sprague Electric Railway and Motor Company in 1888. At Sprague, Emmet worked on the installation of electric street railway systems in several cities, including Cleveland, St. Louis, Wichita, and Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. Subsequently, he worked briefly for the Westinghouse Electric and Manufacturing Company and for the Buffalo Railway Company, before joining the Edison General Electric Company as district engineer in the Chicago district in 1891. When the General Electric Company (GE) was formed through a merger of Edison General Electric and Thomson-Houston, Emmet became a GE employee and was assigned to the Lighting Department in Schenectady, New York, in 1894.
Emmet made significant contributions to ac power systems including the design of large rotary converters which were used widely to convert transmitted ac power to direct current needed for the manufacture of aluminum, electric railways, and other applications. He was a leader in constructing the second largest power generating plant at Niagara Falls, New York, which used GE apparatus.
His career was interrupted by the Spanish-American War when he served as a navigational officer on the collier Justin. When he returned to GE, he was assigned to help develop the steam turbine which began to supplant reciprocating steam engines in the power generating field in the first decade of the twentieth century. Emmet directed the construction and installation of a 5,000 kW turboalternator at the Fisk Street power plant of the Chicago Edison Company in 1903.
Emmet became a leading advocate of the electric propulsion of ships and his efforts led to a GE contract to equip the Navy collier Jupiter with turboelectric drive. The Jupiter proved quite successful during World War I and later was converted into an aircraft carrier and renamed the Langley. In 1915, GE received a contract to install the Emmet propulsion system on a new battleship, the New Mexico, known initially as the California. First tested in sea trials in 1918, the ship's propulsion system, could deliver up to 32,000 hp and achieve a speed of 21 kn. Subsequently, GE installed an even more powerful drive system in high-speed battle cruisers known as the Saratoga and the Lexington. These ships, later converted to aircraft carriers, were designed with 180,000 hp turboalternator propulsion and a speed of 35 kn. During World War I, Emmet served as a member of the Naval Consulting Board formed to provide expert advice on military innovations.
Toward the end of his career, Emmet devoted a great deal of time and energy to the development and promotion of mercury vapor turbine, "as a more efficient power generation system than steam turbines." A few mercury turbines were installed as a result of his efforts but the difficulties and risks in using the new technology led to termination of the development after his retirement.
He received the prestigious Edison Medal of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers in 1919 'For inventions and developments of electrical apparatus and primo movers.' He received the Elliott Cresson Medal of the Franklin Institute in 1920 and also was elected to the National Academy Sciences.
Emmet published The Autobiography of an Engineer in 1931. The book provided a personal account of his career of almost half a century devoted to electrical power engineering. In the preface, Emmet characterized engineering as a "thrilling profession to those who are suited to it, full of dangers, hopes, worries, and gratifications." Later in the book, he attributed much of his success to "a definiteness of purpose backed by a dogged perseverance." He added that "the important part of engineering is the detail and the good engineers are those who keep their eye close to it." He mentioned that he had always had a keen interest in other areas than engineering including literature, history, science, philosophy, music, and art in various forms." Emmet never married. He died on 26 September 1941 at age 82.
Additional Information and Professional Honors
(A'93, M'94, member for life)
Honorary Member 1933
Edison Medalist 1919
AT THE time William LeRoy Emmet began his career in the electrical industry some 50 years ago, he was noted for his desire to explore new fields of engineering, rather than to work in those in which considerable development work had been done. This characteristic has continued throughout his life. Doctor Emmet was born in Pelham, N . Y., July 10, 1859. In 1881 he graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy, remaining in the Navy for 2 years thereafter. In 1887 he joined the Sprague Electric Company, then engaged in the historic electric railway developments at Richmond. Va., and at other cities. After short periods with the Westinghouse Electric and Manufacturing Company and the Buffalo (N.Y.) Railway Company he went to Chicago as district engineer for the newly formed Edison General Electric Company. In 1892 he was transferred to the New York office of the company, which later became the General Electric Company. In 1900 Doctor Emmet started his work on the Curtis steam turbine, and he continued its development until recent years, when his attention turned to the mercury vapor power process in which activity he has again been singularly successful. He is now a consulting engineer of the General Electric Company. Doctor Emmet was elected an Honorary Member of the Institute May 22, 1933, and in 1919 received the Edison Medal. Other medals have been awarded him. He has served the Institute on several of its committees, and was vice-president 1900-02. He is also a past vice-president of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Further Reading
Papers of W.L.R. Emmet - records and correspondence, 1893 - 1941
"W. L. Emmet, 82, Engineer, Is Dead," New York Times, Sep. 27, 1941.