Voltaic Pile
Voltaic Pile
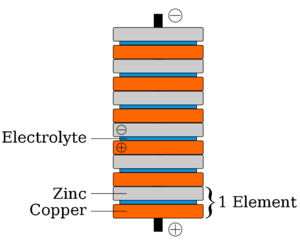
The Italian inventor Alessandro Volta invented the first battery in 1799. Volta’s battery was called a “pile” and was a stack (or pile) of discs made of two types of metal—one silver, the other zinc. The discs were separated from each other by a piece of cloth or cardboard that had been soaked in salt water. Volta found that this wet stack of “dissimilar metals” created a small electric current, and this current could be drawn off through wires and used for experiments. However, a pile could generate only a small voltage of 1-2 volts. Several piles—a “battery” of them—could be assembled side by side and connected to each other with metal strips to create a high power energy source. Volta gave his name to units of electrical energy, the “volt.”
Further Reading
Volta's Electrical Battery Invention, 1799 - Recognized as an IEEE Milestone