Daniell Cell: Difference between revisions
From ETHW
No edit summary |
m (Text replace - "[[Category:Power,_energy_&_industry_application" to "[[Category:Power,_energy_&_industry_applications") |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''''This article is a stub. You can help the GHN by expanding it.''''' | <p>'''''This article is a stub. You can help the GHN by expanding it.''''' </p> | ||
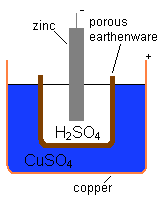
<p>[[Image:Daniel cell.png|thumb|left|Diagram of a Daniell cell]]</p> | |||
[[Category:Power | [[Image:Daniell.jpg|thumb|right|John Frederic Daniell]] | ||
[[Category:Electrochemical_devices_ | |||
<p>London, England. A great advance in battery technology was the invention of what came to be known as the Daniell cell, which John Frederic Daniell made public in 1836. It was the first reliable source of electric current. </p> | |||
[[Category:Power,_energy_&_industry_applications]] | |||
[[Category:Electrochemical_devices_&_processes]] | |||
[[Category:Batteries]] | [[Category:Batteries]] | ||
Revision as of 13:36, 13 November 2013
This article is a stub. You can help the GHN by expanding it.
London, England. A great advance in battery technology was the invention of what came to be known as the Daniell cell, which John Frederic Daniell made public in 1836. It was the first reliable source of electric current.